Have you ever looked at a map and wondered how it was made? Well, one of the ways we create maps is by using something called a Geographic Information System, or GIS for short.
Geographic Information System, commonly known as GIS, is an innovative technology that has revolutionized the way we analyze and manage spatial data.
The Full Form of GIS is “Geographic Information System,” which is a powerful tool used for storing, analyzing, and manipulating geographical data.
GIS is a multi-disciplinary field that combines geography, cartography, statistics, computer science, and data management.
The Geographic Information System goes beyond just creating maps; it provides a platform for complex analysis of spatial data, creating models, and predicting future trends.
What Is A GIS – Geographic Information System Definition?
Geographic Information System, or GIS for short, is a powerful tool that has transformed the way we work with geographical data. At its core, GIS is a computer-based system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, and present data that is related to specific locations on the Earth’s surface.
The Geographic Information System, encompasses a wide range of techniques and technologies that allow us to represent and analyze spatial relationships between different data sets, such as maps, aerial photographs, satellite images, and sensor data.
What Do GIS Means?
To understand GIS, we can define it in three terms: One is Geographic, another one is Information and the third is System.
GIS is a computer-based information system designed to accept large volumes of spatial data or geographic data. These Data are converted into information through computers.
GIS is a generic terms implying the use of Computers to create and display Digital Maps. It produce maps and reads maps.
The main purpose of GIS is not to store the data or keep the data but to provide analysis. This allow us to manipulate, we can edit, and we can visualize important things.
Its major advantage is that it permits us to identify spatial relationships between different map features.
Definition of GIS
It is said that any digital data containing location based information is called GIS. There are many different definitions of GIS, as different users stress different aspects of its uses.
But, you are here to know, what most people think about GIS and want to learn more about it. Below are some Geographic Information System Definition.

The United States Geological Survey (USGS) defined GIS as:

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) defined GIS as:

How GIS Works?
GIS works by integrating spatial data with non-spatial data to create a comprehensive view of an area. Below process allows you to apply GIS to any problem that require a GIS based decision?
- Create and Manage Data – Spreadsheets, tables and raster data with geographic components that ties the data to a particular location. All information in GIS must be linked to a spatial references.
- Do Analysis – GIS software allows users to perform spatial analysis, such as buffering, overlaying, and spatial querying. These techniques allow users to analyze the relationship between different types of data and make informed decisions.
- Maps – Maps are shareable and contain geographic layers. They consists of points, lines and area elements. Maps can be created as and when needed.
- Apps – Mobile GIS Applications allows us to collect and use GIS data anywhere, at any time.
Why Do We Need GIS?
Geographic Information System is becoming vital to understand and make better decisions. It will allows us to check, what is happening in a specific area and once we recognize, we can take corrective actions.
GIS providing us to predict something which has not happened on the ground. That means you can simulate lot of real things and scenarios, which relate to nature.
A GIS combines two different types of information: spatial data (spatial coordinates) and attribute data (descriptions).
Spatial data includes measurements such as latitude and longitude. Attribute data is information that describes the attributes of places or features on a map such as population density.
Any object on the earth can defined with geographic coordinates, which we know as latitude and longitude.
These imaginary grid of latitude and longitude are overlay on entire earth surface. Thus each object on the surface of the earth can assigned these coordinates.
The advantage with the geographic system is that, we can not only assign the coordinates but we can handle all kinds of maps and data.
What Geographic Information System Can Do?
Today GIS is used as a most powerful tool for decision making that have a huge range of applications.
With GIS, we can analyze topographic, demographic, environmental and land use data to help in better business decisions.
GIS can be used to transform business. It help people see better future. Geographic Information System can be used to predict the future to make life-saving decisions to change our world.
A Complete GIS must answer below basic questions. These are:
- Mapping Where Things Are: It helps us to map spatial location and visualize the spatial relationship among the real world features.
- Mapping Densities: We can also map concentrations, or a quantity of spatial data for a specified area.
- Mapping Quantities: GIS can help us to find best places that meet our requirement for our business promotions. We can identify where the actual conditions exist?
- Change Detection: We can map the change in a particular area of feature to anticipate future conditions.
For example, land use changes can be monitored using remote sensing technology. We can easily visualize the changes over different time frame.
Uses of GIS – Geographic Information System?
Almost anything happens somewhere on the earth, knowing wherever some things happen is vital. The importance of GIS, lies in its ability to compute vast amount of information and solve complicated problems.
GIS can be used to identify problems, Monitor Changes, Manage and respond to an events, Do Analysis, and understand Trends.
Scope of GIS is unlimited. Some of the domains are:
- Resource Management – Electric and Gas Utilities.
- Land Use Planning and Civil Engineering.
- Location of Volcanoes – Environment Impact Analysis.
- Economic Development and Businesses Promotion.
- Transportation Routing.
- Historical Data Management.
- Fiber Network Management – GIS In Telecommunications.
- Public Safety Operation like Emergency Operations – Fire, Police and also Weather Risks.
- Incidents, like Crime Statistics.
All of these domains requires Geographic Information System based information outputs. In terms of Application of GIS, the scope is unlimited for GIS Uses.
History of Geographic Information System – GIS
The earliest example of GIS we can see, in 1854 Mr. John Snow created a map of the distribution of cholera outbreak.
Due to this GIS Mapping, Government officials were able to determine the cause of the disease. which is a contaminated water from a pump.
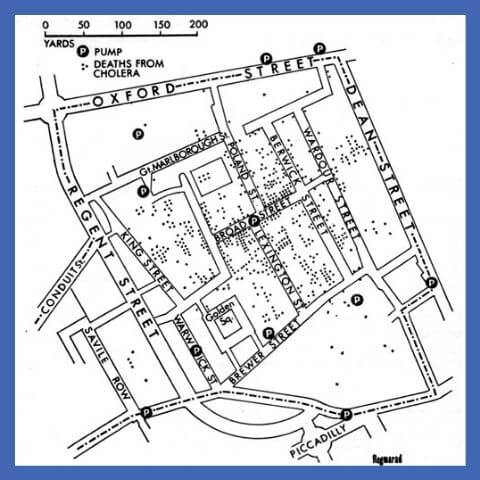
The work of John Snow incontestable that GIS could be a problem-solving tool. He places geographic layers on a paper map and created a life-saving discovery.
In 1968, Roger Tomlinson was the first to use the term “Geographic Information System”. At this time, he was working for the Canadian Government. GIS actually became a computer-based tool for storing map Information.
Mr. Roger Tomlinson can forever remembered as the “Father of GIS”.
Component of Geographic Information System
Now the next step is to understand the areas of GIS and how they work with each other. In this section we will learn the importance of GIS components.
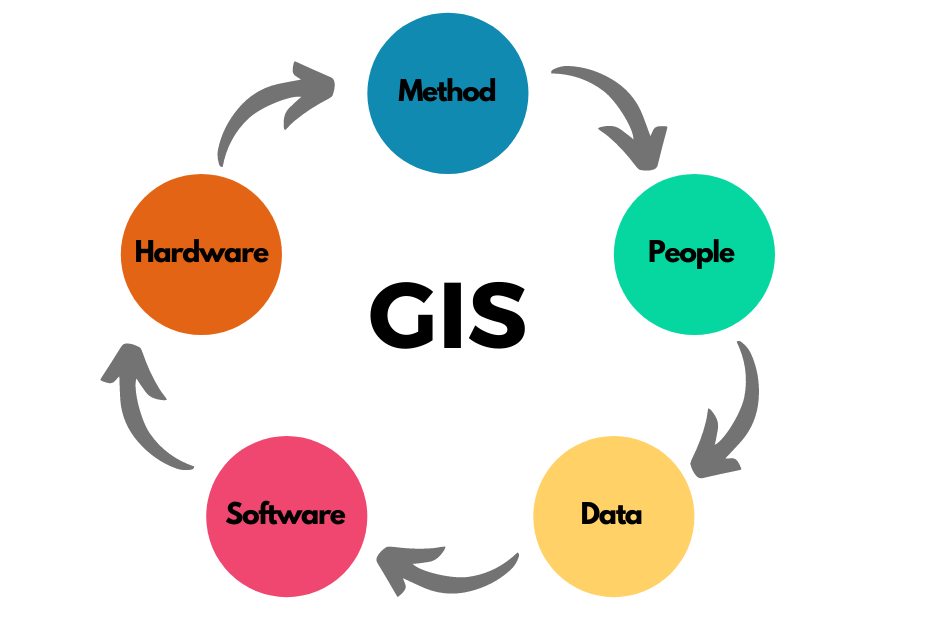
A Geographic Information System is not only about Computers, Software, and Electronic Data.
A working GIS integrates five key components. GIS is an organized collection of Hardware, Software, Data, People and Methods. These Components work together disseminate information about areas of the Earth.
Let’s look at each Components of GIS in more details.
#1: Hardware
Hardware refers to the computer platform and peripherals on which a GIS operates. Today, GIS runs on a large range of computer hardware, it might be a Laptop, Desktop or based on a Centralized Server.
Hardware can also refer to servers either at your office or in the cloud. It can also include a Scanner, digitizer and a Plotter.
To perform well, all hardware component must have high capacity. In simple words: These are the GIS equipment’s that are needed to perform GIS related task.
In case of Hardware, Size and Speed matter a lot. GIS system are very large and complex. The larger and faster your computer, it will respond while performing complex queries.
#2: Software
It Includes your Operating System and GIS Software. It can be either Commercial GIS Software or Open Source GIS. These Open Source Software offered for free of charge.
Commercial Software are copyright protected and are often costly. Currently offered Commercial GIS Software includes ArcGIS, MapInfo, Global Mapper, Geomedia etc.
Out of these, ArcGIS is the most liked software and the Best Open Source Software is QGIS or Quantum GIS.
Web GIS Software also helpful, which provide support and server data through internet browser.
#3: Data
The data component of GIS is arguably the most important. Related Information can be collected in-house or bought from a Commercial Information provider.
GIS Data can come from many forms, including maps, satellite imagery, census data, and geological data. There are two primary types of GIS Data that we use: Raster Data and Vector Data.
GIS data can be collected using various methods such as remote sensing, GPS, and surveying.
Spatial Information can be in the form of a map or raster like Satellite imagery and Aerial Photography. Before proceeding further, these imagery need to georeferenced (latitude/longitude).
Tabular information can be in the form of attribute data. They must associated with the spatial information. Almost every GIS software comes with DBMS support to manage information.
#4: GIS User
In fact, Users are the most important Components of GIS. The proper use of GIS depends on the people performing the analysis.
GIS is a collaborative effort that requires skilled professionals with different backgrounds. The people component of GIS includes GIS analysts, data scientists, programmers, cartographers, and database administrators. These professionals work together to create, manage, and analyze GIS data.
#5: Methods
GIS procedures refer to the processes and methodologies used to create, manage, and analyze GIS data.
This includes data collection, data storage, data manipulation, and data analysis. GIS procedures must be carefully planned and documented to ensure the accuracy and reliability of GIS data.
You can perform GIS Analysis as automated or manual or may be a combination of both. Methods can include templates or requirements that are specific to an organization.
Types of GIS – [Geographic Information System Definition]
The geographic entities or object in GIS based on spatial and thematic data types. The spatial data types consist of geometric and topological data.
The Geometric Data are positional or shape data like coordinates and line. Topological Data contains relationship among geometric data.
There are Two Categories of GIS Data formats: Raster and Vector.
A GIS should be capable of using both raster and vector data. Any real world situation can be represented in digital form in both Raster and Vector formats.
#1. Raster Data
In Raster – objects represented as Grid of Cells or Pixels.
Raster format is more appropriate for data capture task. For Example: Remote Sensing and Image Processing.
#2. Vector Data
In Vector format features represented as Points, Line and Area (Polygon).
These are more accurate and required less space for storage than Raster data.
GIS Software
Choosing the right GIS software is about understanding the problems that you are looking to solve.
There are a variety of Geographical Information Systems (GIS) software offered nowadays. They vary from high-powered analytical software package to visual web applications. Each of these used for a distinct purpose.
GIS software allows to produce maps and other graphic display of information. It allows to visualize the spatial data or to build decision support system.
If you are looking for GIS Software for the first time, then there are different Types of GIS Software available to choose from.
#1. Desktop GIS
Most of the user use Desktop GIS Software for creating, editing and analyzing geographical data.
There are many Desktop GIS Software ranging from free or open source solutions to expensive commercial products. The best example are: QGIS and ArcGIS.
#2. Web Based GIS
Today Internet has completely revolutionized GIS platform. Web GIS gives a non GIS users the ability to interact with Map and answer their own question.
User can access these web based GIS from anywhere, anytime by using their internet browser. Some of the example are: Google Maps, Bing Maps or openstreetmap.org.
#3. Server Based GIS
Generally, they used only for large scale mapping. Example of Server Based GIS Application are: Map Server, GeoServer and ESRI ArcGIS Server.
ESRI ArcGIS Server is one of the most popular server based GIS applications that was developed by ESRI. It’s an industry standard and has been used by enterprises and organizations all over the world.
Using Server Based GIS Server, businesses can track customers’ movements in real time, monitor traffic patterns in their region or even coordinate with transportation providers to make up-to-date signs available to drivers on the road.
#4. Geo Browser Or Web Browser Based Apps
These types of application have the advantage of large user communities. Examples are: Google Earth Web and ArcGIS Earth.
These web-based applications offer a lot of advantages for both businesses and individuals. Web Browser Based GIS Application allows user to interact with a GIS map of any data that has been loaded into it.
Career In GIS
A Geographic Information Systems (GIS) professional is someone who manages, analyzes, maps, generates, interprets and shares geographic information. A GIS professional can work with all kinds of data including but not limited to Census Bureau data, water resources data, and demographic and socioeconomic information.
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) are becoming more popular because they are an essential tool for making sense of the world. The GIS field is one of the most diverse and fastest-growing industries in the world.
Career Path In Geographical Information Systems
Geographical Information Systems (GIS) are becoming more popular because they are an essential tool for making sense of the world.
Different career paths in GIS are open to those interested in working within this systems, including the training required for each one. It will also provide information about how much money one can expect to earn in their chosen field.
GIS Careers for All Skill Levels
There are many different skillsets for GIS careers, including cartography, GIS Analyst, data management, GIS technician, GIS Manager and GIS educator.
These positions typically require a bachelor’s degree or higher but some positions do not require any formal education at all.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts that the employment of GIS professionals will grow by 12% from 2018-2028 while employment of data analysts will grow by 17%.
Best Geography Degrees For Geographic Information System Professionals
There are many different areas of geography to choose from; however, when it comes to an undergraduate degree, you will find that the majority of universities offer degrees in Geography and Environmental Studies.
A Geographic Information Systems (GIS) degree can be obtained at a number of institutions such as The University of Arizona.
A GIS program covers a range of topics including Geographic databases, Global Positioning Systems (GPS), Remote Sensing and Cartography. This is not an exhaustive list but you get the idea: GIS degrees cover a lot!
Geographic Information Systems professionals are in demand in the job market. The degree you earn will depend on your chosen specialization.
If you want to work with maps, cartography, and geographic information systems, you should consider earning a degree in cartography or GIS.
Fundamental of GIS Video Tutorial
You can also watch below Video related to Geographic Information System.
Summary: Geographic Information System Definition – GIS
You must have seen that, when we used to Draw Maps on paper, it is a tedious job. We used to face a lot of problems, but GIS has made our work very easy.
Now we can use GIS Software to design our map and save our data in tabular format.
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are essential tools for understanding our relationship with the environment and how it has changed over time. There are a number of applications that help us use this technology such as Mapbox, Google Earth, and ArcGIS to name a few.
More Related Articles (Geographic Information System Definitions)
FAQ: Geographic Information System Definition
What Does GIS Mean In Geography?
Geographic information systems (GIS) is a system of capturing and storing data and assigning spatial coordinates to this information. It is a broad term that encompasses many different types of disciplines.
How Does GIS Apply To Geography?
Geographers are now able to use GIS to map data in order to find patterns, trends, and changes in the environment.
Geographers have traditionally relied on maps for their work. They used them to track changes in the environment, measure distances between countries, and even predict natural disasters. Now they can also use geographic information systems (GIS) to map data and find patterns that help them analyze the world around them.
Why GIS Is Important?
GIS is an acronym for Geographic Information System. GIS is an important tool in many fields like business, engineering, mapping, and education.
It allows you to visualize data on a map and do spatial analysis. With the help of real-time satellite imagery or aerial photography, people can monitor changes on the Earth’s surface such as urbanization or deforestation over time.
What Is A Feature In GIS?
A feature is a point, line, or area on the earth’s surface that has been assigned a unique identifier. These features can be represented as points, lines or areas on a map. They consist of coordinates and attributes such as elevation and land cover type.
What Is A Layer In GIS?
A layer is a set of features within the GIS system. Layers can be used to represent different aspects of the geography of an area.
Layers are used to organize geographic data into manageable groups that contain related information about the subject. A layer can show different types of features, such as roads or water bodies, and is often composed of datasets that are shared by many other layers in the map.
What Is A Coordinate System In GIS?
Coordinate systems are used to describe positions on a map. The most common coordinate system is the Latitude and Longitude.
How To Learn Geographic Information System?
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are the most important data sources for spatial analysis. GIS is an evolving field with a number of challenging opportunities for spatial data collection, modelling, and understanding the interaction of natural and human phenomena.
A GIS course can be taken online, through a local college or university, or through an online course provider. The key to learning Geographic Information Systems is to have a strong foundation in cartography, geographic information science, geography, mathematics, cartography skillsets and computer science.
What Is GIS Programming?
Geographic Information System programming is a branch of computer programming in which programmers can manipulate data with the help of code. These programmers are able to store the data in grids, and they are also able to use functions that can be programmed to work with this data.
How Expensive Is GIS?
Geographic Information Systems are important for understanding the geography of a specific location.
The cost for Geographic Information Systems can vary depending on what kind of system you buy, where you buy it from, and how many different types of data you would like to have access to.
I may choose Open Source GIS Application for your organization.
Why Do Geographers Use GIS?
Geographic Information Systems are used by geographers to generate maps of their area of study.
Firstly, GIS is able to show the relationships between spatial and non-spatial phenomena. Secondly, it can be used in a variety of different ways, such as to visualize patterns in spatial data and create geographic representations of abstract data. And lastly, it has an active and expanding user base that is developing new web-based tools and applications every day.
What GIS Software Used The Most?
Geographical information systems are used for many purposes. They are being used to monitor wildfires, map the impacts of climate change, solve crimes and much more.
ESRI is one of the leading providers of GIS software. ESRI provides mapping platforms for enterprises that want better location data. ArcGIS and QGIS are the most used gis software currently around the world.
Why Are GIS Maps Useful?
Maps are useful because they can help us understand our surroundings better. The maps can be used to take a tour of the country, explore different cities, or find out where an address is.

Wrong spelling on image
Thanks,
Spelling Corrected and Blog also updated with relevant Images and Videos.