In the world of advanced technology and precise measurements, two terms often surface – Lidar and Laser. While they may seem similar at first glance, they serve distinct purposes and find their applications in various industries. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the differences between Lidar and Laser (Lidar vs Laser) and explore the vast range of industries where they play pivotal roles.
Lidar and Laser differ in their core functions. Lidar is a remote sensing technology that measures distances using laser light, often used for mapping and environmental applications. Laser, on the other hand, is a focused beam of light used for cutting, welding, and medical procedures, emphasizing precision and energy delivery.
Difference Between Lidar and Laser
In a rapidly evolving technological landscape, precision and accuracy are paramount. Lidar and Laser technologies are at the forefront, each offering unique capabilities that have revolutionized various industries. Let’s embark on a journey to understand the differences, applications, and potential of Lidar and Laser.
What is Lidar?
Lidar, short for “Light Detection and Ranging,” is a remote sensing method that employs laser light to measure distances with exceptional precision. It works on the principle of emitting laser pulses and measuring the time it takes for the light to bounce back after hitting an object. Lidar is widely used in applications such as autonomous vehicles, archaeology, forestry, and environmental monitoring.
How Does Lidar Work?
Lidar systems emit laser pulses towards a target surface and measure the time it takes for the laser beams to bounce back. By calculating the round-trip travel time and knowing the speed of light, Lidar systems can accurately determine the distance between the sensor and the target. This process creates a point cloud of data, which is then used to generate detailed 3D maps or models of the environment.
The interaction of LiDAR with other ranging technologies, such as radar and sonar, further enhances its utility. To understand how LiDAR complements radar technology, you can learn more about the differences between LiDAR and radar
Applications of Lidar
Lidar has a diverse range of applications:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Lidar sensors help self-driving cars navigate and detect obstacles.
- Archaeology: Lidar is used to create high-resolution maps of archaeological sites, revealing hidden structures.
- Forestry: It aids in forest inventory, monitoring tree health, and assessing deforestation.
- Environmental Monitoring: Lidar is crucial for studying the Earth’s surface, from glaciers to coastal areas.
Pros and Cons of Lidar
Pros:
- Exceptional accuracy in measuring distances.
- Vital for autonomous vehicles.
- Precise mapping for various applications.
Cons:
- Can be costly.
- Sensitive to adverse weather conditions.
- Limited range in certain situations.
What is Laser?
Laser, which stands for “Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation,” is a coherent and focused beam of light with specific properties like directionality and monochromaticity. Unlike Lidar, Laser technology is primarily used for cutting, welding, engraving, and medical procedures, where precise energy delivery is essential.
How Does Laser Technology Work?
Laser devices generate laser light through a process of amplifying photons using stimulated emission. The resulting laser beam is highly directional and focused, making it suitable for various applications, including cutting, engraving, and communication.
Applications of Laser
Laser technology has found its place in several fields:
- Manufacturing: Laser cutting and welding are essential in various manufacturing processes.
- Medicine: Lasers are used for surgical procedures, eye surgeries, and dermatology treatments.
- Communications: Optical fiber communication relies on lasers for data transmission.
- Entertainment: Lasers are used in light shows, laser tag, and even laser pointers.
Pros and Cons of Laser
Pros:
- High precision in various applications.
- Efficient energy delivery for cutting and welding.
- Versatile use in science and technology.
Cons:
- Potential for eye damage if not used cautiously.
- Limited to line-of-sight applications.
- Limited range in open air.
Lidar vs Laser: How Do They Work?
Lidar relies on the measurement of the time it takes for laser pulses to return after hitting objects. This data is then processed to create detailed 3D maps or models of the environment. Laser, on the other hand, emits a concentrated beam of light that can be used for various purposes, including cutting, marking, and measuring.
Contrasting Lidar and Laser
Now that we’ve gained insights into both Lidar and Laser technologies, let’s highlight their key differences:
| LiDAR | Laser |
|---|---|
| Remote sensing technology | Generates a coherent beam of light |
| Uses laser light to measure distances | Technology used within LiDAR systems |
| Creates high-resolution 3D maps | Used in various applications beyond sensing |
| Considered more accurate | Has diverse types with different properties |
Principle of Operation
- Lidar relies on the emission and detection of laser pulses for distance measurement.
- Laser technology generates a concentrated, coherent beam of light with various applications.
Applications
- Lidar is predominantly used in remote sensing, mapping, and environmental monitoring.
- Laser technology finds applications in surgery, manufacturing, communication, and entertainment.
Precision
- Lidar is known for its high precision in measuring distances and creating detailed 3D maps.
- Laser technology offers precision in cutting, engraving, and other material processing tasks.
Industries
- Lidar is commonly used in geospatial, automotive, and environmental sectors.
- Laser technology spans across medical, industrial, and entertainment industries.
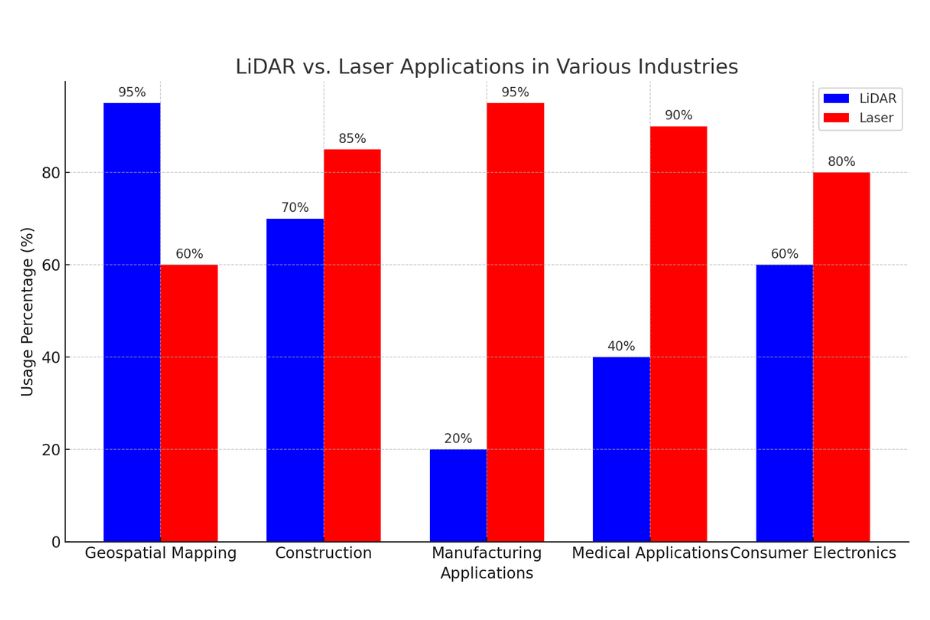
The bar chart above visualizes the hypothetical usage percentages of LiDAR and laser technologies across different industries. It highlights LiDAR’s predominance in geospatial mapping due to its precision in capturing 3D data, while lasers are more commonly used in construction and manufacturing for their precision and power. In medical applications and consumer electronics, lasers are favored due to their ability to be miniaturized and used in delicate, precise tasks.
Future Trends
Both Lidar and Laser technologies continue to evolve. Lidar is becoming more affordable, expanding its applications, and laser technology is finding new applications in fields like quantum computing and materials science.
Conclusion
In the world of Lidar vs Laser, it’s not a matter of one being better than the other; rather, it’s about choosing the right tool for the job. These technologies have redefined precision in various industries and will continue to do so in the future.
Understanding the differences between Lidar and Laser is crucial for harnessing their full potential and making informed decisions in choosing the right technology for specific applications.
FAQs: Lidar Vs Laser
Is Lidar the same as Laser?
No, Lidar is a remote sensing technology that uses laser light, while Laser is a focused beam of light used for various purposes.
Which technology is better for medical procedures?
Laser technology is preferred for medical procedures due to its precise energy delivery.
Can Lidar work in adverse weather conditions?
Lidar can be sensitive to adverse weather conditions like heavy rain or fog.
What is the primary application of Lidar in autonomous vehicles?
Lidar sensors in autonomous vehicles help in obstacle detection and navigation.
