In today’s rapidly advancing technological landscape, sensors play a pivotal role in a wide range of applications, from autonomous vehicles to robotics and even in our smartphones. Two prominent sensor technologies, Lidar (Light Detection and Ranging) and Time-of-Flight (ToF), have garnered significant attention due to their ability to capture depth and distance information. In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Lidar vs. ToF sensors, comparing their working principles, applications, advantages, and limitations. Let’s embark on this journey to understand these fascinating technologies better.
Lidar and TOF (Time-of-Flight) sensors differ primarily in precision and range. Lidar offers millimeter-level accuracy and excels in long-range applications like autonomous vehicles. TOF sensors are more compact, suitable for short to medium-range tasks, and consume less power. Choose Lidar for precision and long distances, TOF for portability and efficiency.
Understanding Lidar
What is Lidar?
LiDAR, an acronym for Light Detection and Ranging, operates by emitting light pulses and measuring the time delay between the emission and reception of these pulses. This principle, similar to radar but using light instead of electromagnetic waves, is utilized in a range of devices, including 2D and 3D laser scanners and Flash Lidars. While traditional LiDAR continuously scans the environment, newer Flash Lidar technology illuminates the entire scene at once, enhancing the frame rate and efficiency for applications like automotive.
Lidar Applications
Lidar technology has found extensive applications in various industries:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Lidar sensors are a crucial component in self-driving cars, enabling them to navigate and detect obstacles with exceptional accuracy.
- Environmental Monitoring: Lidar is used for topographical mapping, forest canopy analysis, and even monitoring air quality.
- Archeology: It aids archaeologists in uncovering hidden structures and landscapes through laser scanning.
- Aerospace: Lidar is used for terrain mapping, obstacle detection, and altimetry in aircraft and drones.
Advantages of Lidar
- Higher Accuracy: Essential for applications requiring detailed spatial data.
- Robustness in Challenging Environments: Performs well in dust or fog.
- Higher Lateral Resolution: Ideal for detailed 3D mapping.
- Higher Frame Rates: Beneficial for dynamic environments.
- Mechanical Robustness: Suitable for outdoor and industrial applications.
Unpacking Time-of-Flight (TOF)
What is TOF?
Time-of-Flight, often referred to as TOF, is another remote sensing technology used to measure distances. TOF sensors emit light or other electromagnetic waves and calculate distances based on the time it takes for these signals to return after hitting an object.
TOF Applications
TOF technology has gained prominence in several industries:
- Gesture Recognition: TOF sensors are used in gaming consoles and smartphones for gesture-based control.
- Camera Autofocus: Many cameras employ TOF sensors to achieve quick and accurate autofocus.
- Robotics: TOF helps robots avoid obstacles and navigate their environments effectively.
- Augmented Reality: It enhances AR experiences by precisely measuring distances and recognizing objects.
Advantages of TOF
- Cost-Effectiveness: More affordable than LiDAR systems.
- Compact Design: Easily integrated into smartphones and other small devices.
- Simplified Pixel Design: Often achieved with standard CMOS processes.
- No Rolling Shutter Effect: Provides synchronously ranged data for all pixels.
- Scalability: Suitable for mass production and diverse applications.
Lidar vs TOF: A Comparative Analysis
Let’s delve deeper into the comparative analysis of Lidar and TOF (Time-of-Flight) sensors, focusing on precision, range, size/portability, and power consumption:
Precision
Lidar sensors are celebrated for their exceptional precision, making them indispensable in scenarios where accuracy is paramount.
They operate on a principle that allows them to achieve millimeter-level accuracy in distance measurements. This precision is especially valuable in applications like autonomous vehicles, where a small measurement error can have significant consequences.
TOF sensors, while accurate in their own right, may not quite reach the same level of precision as Lidar. Their measurements are highly reliable but may not be as finely detailed.
Range
One of Lidar’s standout features is its capability in long-range applications. It excels at detecting objects and gathering data at substantial distances, making it an ideal choice for tasks like aerial mapping, where the ability to cover vast areas is essential.
Autonomous vehicles benefit greatly from Lidar’s extended range, allowing them to identify objects on the road ahead even at high speeds. TOF sensors, on the other hand, are better suited for shorter to medium-range applications.
While they offer excellent performance within their range, they may struggle to maintain accuracy over long distances compared to Lidar.
Size and Portability
When it comes to size and portability, TOF sensors hold a significant advantage. They are typically more compact and lightweight than Lidar systems.
This compactness makes TOF sensors an attractive choice for devices with limited space, such as smartphones, gaming consoles, and small robotics.
Lidar systems tend to be bulkier, which can limit their integration into smaller or more space-constrained devices.
Power Consumption
Power efficiency is a critical consideration in today’s battery-powered devices. TOF sensors shine in this department as well. They consume considerably less power compared to Lidar systems.
This low power consumption is a boon for devices that rely on batteries, as it extends their operational lifespan.
In contrast, Lidar’s higher power requirements can be a limiting factor in devices with limited battery capacity, where conserving energy is a priority.
Lidar Vs TOF Which Is Better?
When it comes to the choice between Lidar and TOF (Time-of-Flight) technology, determining which is better depends on the specific application and requirements. Lidar is renowned for its unmatched precision and long-range capabilities, making it the preferred choice for critical applications like autonomous vehicles and environmental monitoring. Its ability to generate millimeter-level accurate 3D maps is unparalleled.
On the other hand, TOF sensors excel in compactness, real-time measurements, and low power consumption, making them ideal for consumer electronics and robotics. They offer speedy distance calculations, making them suitable for dynamic applications like gesture recognition and camera autofocus.
In essence, there is no one-size-fits-all answer to the “Lidar vs TOF” question. The choice hinges on your project’s unique needs.
For applications requiring utmost precision and long-range detection, Lidar is the frontrunner. Conversely, if compactness, real-time measurements, and energy efficiency are top priorities, TOF sensors hold a distinct advantage. It’s essential to carefully evaluate your project’s demands to make an informed decision between these two remarkable sensing technologies.
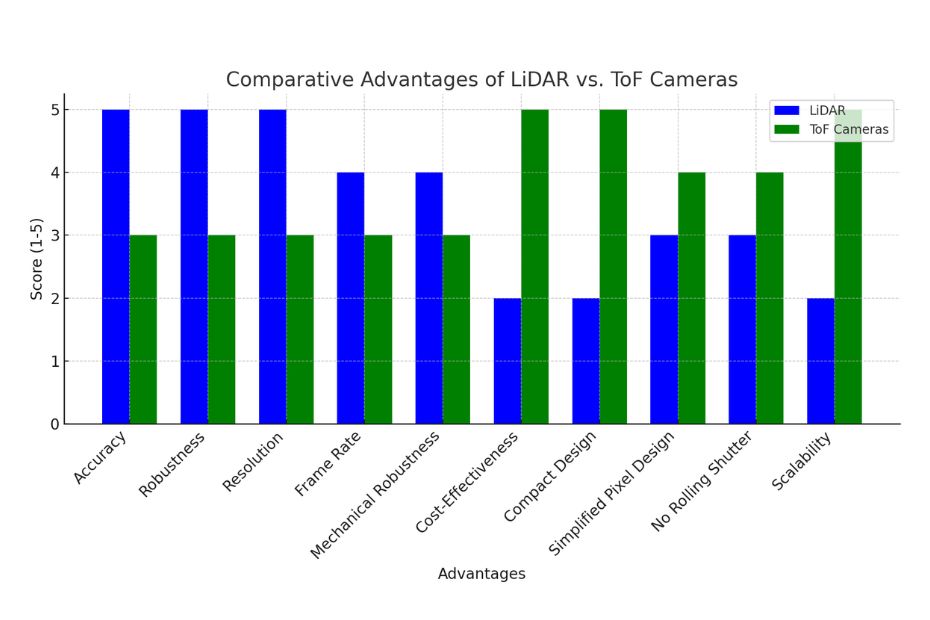
From the chart, it’s clear that LiDAR scores higher in terms of accuracy, robustness in challenging environments, resolution, and mechanical robustness. Meanwhile, ToF cameras excel in cost-effectiveness, compact design, and scalability. Both technologies have comparable scores in aspects like frame rate and pixel design.
Conclusion:
In the Lidar vs ToF debate, the choice depends on the specific requirements of your application. Lidar excels in outdoor scenarios that demand long-range, high-precision sensing, while ToF sensors offer cost-effective solutions for indoor applications and short-range depth sensing.
Both technologies continue to evolve, with ongoing research and development efforts aimed at addressing their limitations and expanding their applications. As the technology landscape progresses, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in Lidar and ToF sensors.
FAQs: Lidar vs ToF
Are Lidar and ToF sensors interchangeable?
No, they are not interchangeable. Their suitability depends on the specific requirements of the application.
Can Lidar work in low-light conditions?
Lidar performance may be affected in low-light conditions, but it generally performs better in such scenarios compared to ToF sensors.
Are ToF sensors only used in consumer electronics?
No, ToF sensors have a wide range of applications beyond consumer electronics, including industrial automation and robotics.
What is the future of Lidar and ToF technology?
The future looks promising for both technologies, with advancements expected in their capabilities and broader adoption across industries.
Which is more cost-effective, Lidar, or TOF?
TOF sensors are generally more cost-effective, making them a preferred choice for applications where cost is a significant factor.