Remote sensing has revolutionized the way we perceive the world, providing us with insights into the earth’s natural processes that were once impossible to obtain. With the rapid advancement in technology, we can now access remote sensing data from various sources without any hassle. This article will discuss the top 10 sources of free remote sensing data, their advantages, and the areas where they can be best utilized.
The Top 10 sources of free remote sensing data are NASA Earth Observation (NEO), USGS Earth Explorer, ESA’s Sentinel data, NASA Earth Data, NOAA Class, NOAA Digital Coast, IPPMUS Terra, LANCE, VITO Vision, GLOVIS.
Top 10 Sources of Free Remote Sensing Data
While remote sensing data is critical, accessing it can be expensive. Fortunately, there are several sources of free remote sensing data available on the internet.
1. NASA Earth Observation (NEO)
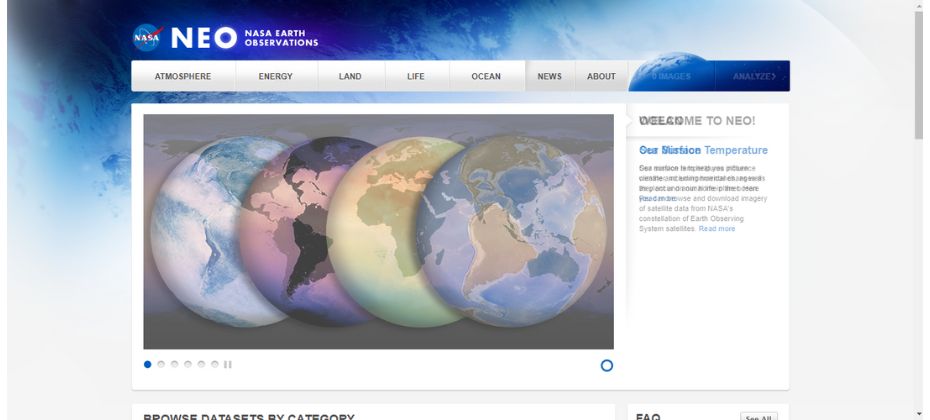
NASA Earth Observation (NEO) is a treasure trove of satellite imagery and remote sensing data. NEO offers daily, weekly, and monthly images captured by various NASA satellites, such as Terra and Aqua. Users can access a wealth of information on climate change, natural disasters, and global ecosystems.
NEO also provides visualization tools that help users understand complex data sets. The platform is user-friendly, making it an excellent starting point for those new to remote sensing. The data is available in various formats, including NetCDF, GeoTIFF, and HDF.
2. USGS Earth Explorer
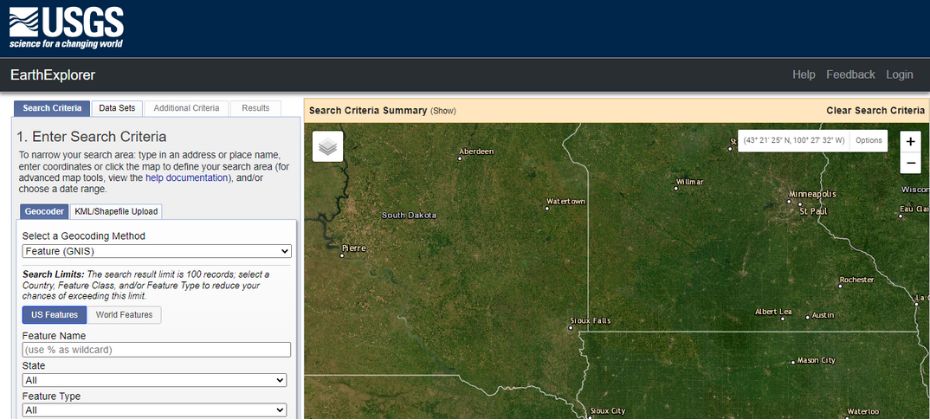
The USGS Earth Explorer is a powerful search platform that provides free access to satellite imagery, aerial photography, and remote sensing data. With its extensive archive, the Earth Explorer offers data from various satellites like Landsat, Sentinel, and ASTER.
One of the platform’s standout features is its customizable search criteria, allowing users to find data based on location, date, and sensor type. The USGS Earth Explorer is a must-visit resource for remote sensing enthusiasts.
3. ESA’s Sentinel Data
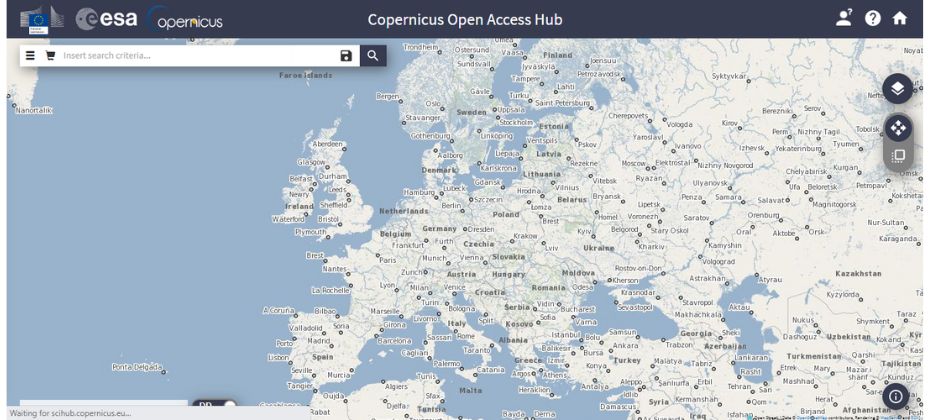
ESA’s Sentinel Data, part of the Copernicus program, offers high-quality remote sensing data from the Sentinel series of satellites. The data is invaluable for monitoring the Earth’s environment, supporting disaster management, and aiding in climate change research.
ESA provides free access to Sentinel data through its Open Access Hub. Users can download and process the data using open-source tools like Sentinel Hub or SNAP. The data is available in various formats, including GeoTIFF and NetCDF.
4. NASA Earth Data
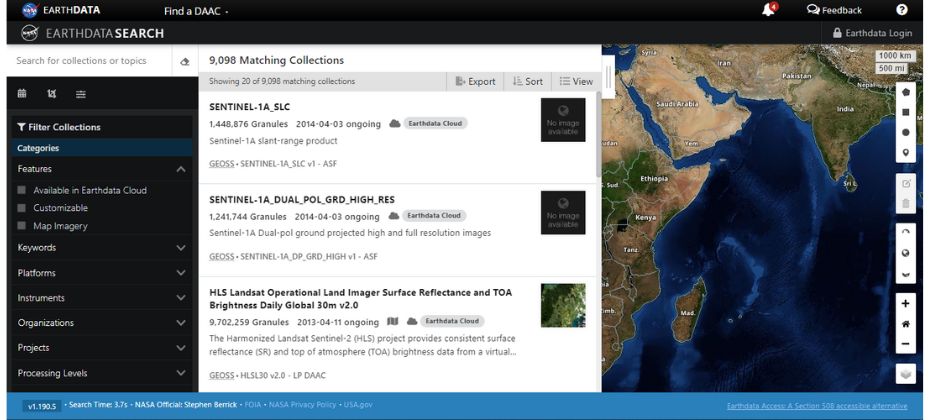
NASA Earth Data is an extensive repository of remote sensing data, tools, and services. It offers data from numerous satellite missions like MODIS, SMAP, and GPM. Users can explore diverse topics such as oceanography, cryosphere, and atmospheric science.
The platform also provides useful data visualization tools like Worldview, which allows users to interact with satellite imagery and data layers in real-time.
5. NOAA CLASS
The NOAA Comprehensive Large Array-data Stewardship System (CLASS) is an archive of environmental data from a variety of sources, including satellite, radar, and in-situ measurements. It covers a wide range of topics, such as weather, climate, and oceanic conditions.
CLASS offers free access to data from various satellite missions like GOES, POES, and DMSP. Users can search and download data through an intuitive interface, making it easy to find the information they need.
6. NOAA Digital Coast

NOAA Digital Coast is a resource for coastal management professionals, providing access to remote sensing data, tools, and training. The platform offers data on shoreline change, sea level rise, and coastal flood hazards.
Digital Coast is not just a data repository; it also offers valuable tools for data visualization and analysis, making it a comprehensive resource for coastal management and research.
7. IPPMUS Terra
IPPMUS Terra is a platform that provides free access to remote sensing data and satellite imagery from various sources, including Landsat, Sentinel, and MODIS. IPPMUS Terra is particularly useful for urban and land use planning, as well as environmental monitoring.
The platform’s user-friendly interface allows users to search for data by location, date, and sensor type. The data can be visualized and analyzed using built-in tools, making IPPMUS Terra a versatile resource for remote sensing professionals.
8. LANCE
NASA’s Land, Atmosphere Near real-time Capability for EOS (LANCE) provides near real-time remote sensing data from a variety of Earth Observing System (EOS) satellites. LANCE is designed to support time-critical applications, such as monitoring wildfires, air quality, and weather events.
LANCE offers free access to data from instruments like MODIS, AIRS, and MLS. The platform is an essential resource for researchers and organizations requiring up-to-date information for decision-making and response.
9. VITO Vision
VITO Vision is a platform offering free access to remote sensing data from the PROBA-V and TROPOMI satellites. These satellites provide vital information on vegetation and air quality, respectively. The data is valuable for environmental monitoring, agricultural management, and air pollution research.
VITO Vision allows users to search for data based on location, date, and product type. The platform also offers visualization tools to help users analyze and interpret the data, making it a valuable resource for remote sensing applications.
10. GLOVIS
USGS Global Visualization Viewer (GLOVIS) is a web-based search and order tool for remote sensing data from various satellite missions, including Landsat, ASTER, and EO-1. GLOVIS is designed to simplify the process of finding and obtaining satellite imagery and data.
The platform offers an intuitive interface, allowing users to search for data by location, date, and sensor type. GLOVIS provides previews of the available imagery, making it easy for users to find the data they need for their remote sensing projects.
Advantages of Free Remote Sensing Data
Free remote sensing data offers various advantages for researchers, scientists, and students. Here are some of the advantages of free remote sensing data:
- Easy Accessibility: Free remote sensing data is easily accessible, allowing users to access valuable data without spending a lot of money. Most of the top sources of free remote sensing data offer easy online access, making it easy to download and use the data.
- Cost-effective: Free remote sensing data is cost-effective, eliminating the need to spend money on expensive data acquisition and processing. This makes it an ideal option for students and researchers who may not have the budget to purchase expensive data.
- Widely Available: Free remote sensing data is widely available, providing access to data from various sources and covering a wide range of applications. This allows researchers to select the best data source for their specific research needs.
- Consistency: Free remote sensing data is often collected by long-term monitoring programs, providing consistent data for temporal analysis. This consistency in the data is essential for research studies that require data from multiple time periods.
- Large Coverage Area: Remote sensing data covers a large area, allowing researchers to study large geographical areas that may be difficult to study using traditional field-based methods.
- Multiple Sensors: Remote sensing data is collected using different sensors, including satellites, aircraft, and ground-based instruments. This allows researchers to select the most appropriate sensor for their specific research needs.
- High Spatial and Temporal Resolution: Remote sensing data offers high spatial and temporal resolution, providing detailed information about the earth’s surface. This high-resolution data is ideal for studies that require detailed analysis of the earth’s surface.
- Timely Data Acquisition: Remote sensing data can be acquired in near real-time, providing researchers with up-to-date information about changes in the environment. This is essential for studies that require timely information, such as disaster management.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, these top 10 sources of free remote sensing data offer valuable information for research and applications across a wide range of fields. With the wealth of data and tools available, there has never been a better time to delve into the world of remote sensing.
The availability of free remote sensing data has revolutionized the way we conduct research, allowing researchers to access valuable data without spending a lot of money.
FAQs: List of 10 Sources of Free Remote Sensing Data
What is remote sensing data?
Remote sensing data is data and information collected from a distance using various sensors mounted on airplanes or satellites. It is used for a wide range of applications, including monitoring weather patterns, tracking natural disasters, managing natural resources, and analyzing urban growth patterns.
Why is remote sensing data important?
Remote sensing data is important because it allows us to collect data and information about the Earth from a distance. This data has a wide range of applications, including monitoring weather patterns, tracking natural disasters, managing natural resources, and analyzing urban growth patterns.
Is remote sensing data expensive?
Accessing remote sensing data can be expensive, but there are several sources of free remote sensing data available on the internet.
What are the advantages of free remote sensing data?
Free remote sensing data provides various advantages, including easy accessibility, cost-effectiveness, wide availability, and consistency.
What are the areas where free remote sensing data can be utilized?
Free remote sensing data can be utilized in various areas, including agriculture, climate change, disaster management, natural resource management, and urban planning.
